Use Sentence Transformers with TensorFlow
In this blog, you will learn how to use a Sentence Transformers model with TensorFlow and Keras. The blog will show you how to create a custom Keras model to load Sentence Transformers models and run inference on it to create document embeddings.
Sentence Transformers is the state-of-the-art library for sentence, text, and image embeddings to build semantic textual similarity, semantic search, or paraphrase mining applications using BERT and Transformers 🔎 1️⃣ ⭐️
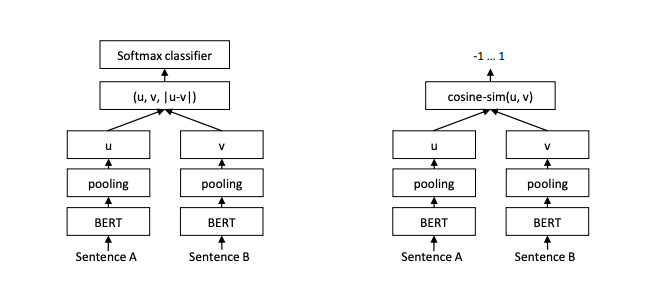
Paper: Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks
The library is built on top of PyTorch and Hugging Face Transformers so it is compatible with PyTorch models and not with TensorFlow by default. But since Hugging Face Transformers is compatible with PyTorch and TensorFlow it is possible to load the raw Sentence Transformer models in Tensorflow.
You will learn how to:
- Setup Development Environment
- Create a custom TensorFlow Model
- Run inference and validate results
- Create e2e model with tokenizer included
Let's get started! 🚀
1. Setup Development Environment
Our first step is to install Transformers, along with tensorflow-text and some other libraries. We are also installing sentence-transformers for later use to validate our model and results.
# installing tensorflow extra due to incompatibility with conda and tensorflow-text https://github.com/tensorflow/text/issues/644
!pip install transformers[tf] -q --upgrade
!pip install sentence-transformers -q # needed for validating results2. Create a custom TensorFlow Model
When using sentence-transformers natively you can run inference by loading your model in the SentenceTransformer class and then calling the .encode() method. However this only works for PyTorch and we want to use TensorFlow. When calling .encode() on your PyTorch model SentenceTransformers will first do a forward pass through the vanilla Hugging Face AutoModel class then apply pooling and or normalization.
This means if we want to use TensorFlow we can create a similar TFSentenceTransformer class, which does the same thing as SentenceTransformer but uses TensorFlow and Keras instead of PyTorch.
Our first step is to create a custom TensorFlow model initalizes our TFAutoModel from Transformers and includes helper methods for mean_pooling and normalization.
Note: We focus in this example only on Sentence Transformers, which are not including any additional layers.
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import TFAutoModel
class TFSentenceTransformer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, model_name_or_path, **kwargs):
super(TFSentenceTransformer, self).__init__()
# loads transformers model
self.model = TFAutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, **kwargs)
def call(self, inputs, normalize=True):
# runs model on inputs
model_output = self.model(inputs)
# Perform pooling. In this case, mean pooling.
embeddings = self.mean_pooling(model_output, inputs["attention_mask"])
# normalizes the embeddings if wanted
if normalize:
embeddings = self.normalize(embeddings)
return embeddings
def mean_pooling(self, model_output, attention_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] # First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = tf.cast(
tf.broadcast_to(tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, -1), tf.shape(token_embeddings)),
tf.float32
)
return tf.math.reduce_sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, axis=1) / tf.clip_by_value(tf.math.reduce_sum(input_mask_expanded, axis=1), 1e-9, tf.float32.max)
def normalize(self, embeddings):
embeddings, _ = tf.linalg.normalize(embeddings, 2, axis=1)
return embeddingsWe can now test our model by selecting and loading a Sentence Transformer from the Hugging Face Hub. We are going to use the sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model, which maps sentences & paragraphs to a 384 dimensional dense vector using mean pooling and normalization.
Note: Different Sentence-Transformers can have different processing steps, e.g. cls pooling instead of mean pooling or an additional dense layer. For this make sure to the check the model repository and adjust the TFSentenceTransformer class."
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
# Hugging Face model id
model_id = 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2'
# Load model and tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
model = TFSentenceTransformer(model_id)
# Run inference & create embeddings
payload = ["This is a sentence embedding",
"This is another sentence embedding"]
encoded_input = tokenizer(payload, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='tf')
sentence_embedding = model(encoded_input)
print(sentence_embedding.shape)
# <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 384), dtype=float32, numpy= array([[[ 3.37564945e-02, 4.20359336e-02, 6.31270036e-02,
# (2, 384)3. Run inference and validate results
After we have now successfully created our custom TensorFlow model TFSentenceTransformer we should compare our results to the results from the original Sentence Transformers model.
Therefore are we loading our model using sentence-transformers and comparing the results.
import numpy as np
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
compare_input = "This is a sentence embedding, which we will compare between PyTorch and TensorFlow"
# loading sentence transformers
st_model = SentenceTransformer(model_id,device="cpu")
# run inference with sentence transformers
st_embeddings = st_model.encode(compare_input)
# run inference with TFSentenceTransformer
encoded_input = tokenizer(compare_input, return_tensors="tf")
tf_embeddings = model(encoded_input)
# compare embeddings
are_results_close = np.allclose(tf_embeddings.numpy()[0],st_embeddings, atol=7e-8)
print(f"Results close: {are_results_close}")
# Results close: TrueThe created sentence embeddings from our TFSentenceTransformer model have less then 0.00000007 difference with the original Sentence Transformers model. This is good enough to validate our model.
4. Create e2e model with tokenizer included
One difference between the original Sentence Transformers model and the custom TensorFlow model is that the original model does include a tokenizer. This is not included in the custom TensorFlow model.
The orginial sentence transformer model is using AutoTokenizer to tokenize the sentences as well meaning it is not included in our model graph. But we can create a custom model for BERT that includes FastBertTokenizer from TensorFlow Text. This will allow us to use the tokenizer in our model graph.
The FastBertTokenizer got integrated into transformers as TFBERTTokenizer and works with the Hugging Face assets.
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import TFAutoModel, TFBertTokenizer
class E2ESentenceTransformer(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, model_name_or_path, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
# loads the in-graph tokenizer
self.tokenizer = TFBertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, **kwargs)
# loads our TFSentenceTransformer
self.model = TFSentenceTransformer(model_name_or_path, **kwargs)
def call(self, inputs):
# runs tokenization and creates embedding
tokenized = self.tokenizer(inputs)
return self.model(tokenized)We can now create our E2ESentenceTransformer model that includes the tokenizer and run inference on it.
# hugging face model id
model_id = 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2'
# loading model with tokenizer and sentence transformer
e2e_model = E2ESentenceTransformer(model_id)
# run inference
payload = "This is a sentence embedding"
pred = e2e_model([payload]) # Pass strings straight to model!
print(f"output shape: {pred.shape}")
e2e_model.summary() # prints model summary
# output shape: (1, 384)
# Model: "e2e_sentence_transformer_30"
# _________________________________________________________________
# Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
# =================================================================
# tf_bert_tokenizer_30 (TFBer multiple 0
# tTokenizer)
#
# tf_sentence_transformer_59 multiple 22713216
# (TFSentenceTransformer)
#
# =================================================================
# Total params: 22,713,216
# Trainable params: 22,713,216
# Non-trainable params: 0
# _________________________________________________________________Conclusion
Thats it. We have now successfully created a custom TensorFlow model that can load a Sentence Transformer model and run inference on it to create document embeddings. This will allow you to integrate Sentence Transformers into your existing and new TensorFlow projects and workflows. We validated that our model creates embeddings that are similar to the original Sentence Transformers model.
And as bonus we looked into how to integrate the tokenization into our model graph as well and created an E2ESentenceTransformer model that includes the tokenizer for BERT models, which are achieving state-of-the-art performance on similar tasks.
If you are interested in how to deploy those models with TFServing let me know!
Converting SentenceTransformers to Tensorflow is another source by Edward Ross.
Thanks for reading. If you have any questions, feel free to contact me, through Github, or on the forum. You can also connect with me on Twitter or LinkedIn.