Introducing MCP CLI: A way to call MCP Servers Efficiently
Updated January 2026 for v0.3.0 — New 3-subcommand architecture (
info,grep,call), connection pooling daemon, and tool filtering support.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard for connecting AI agents to external tools, APIs, and data sources. However, as the ecosystem grows with more powerful MCP servers, developers and agent builders are hitting a scaling bottleneck: context window bloat.
mcp-cli is a lightweight CLI that allows dynamic discovery of MCP, reducing token consumption while making tool interactions more efficient for AI coding agents.
Key Features:
- 🪶 Built on Bun,
mcp-clicompiles to a single standalone binary. - 🔌 Works with both stdio (local) and HTTP (remote) MCP servers.
- 🔍 Glob-based search across all servers
mcp-cli grep "*mail*" -d. - 🤖 Designed for AI coding agents (Gemini CLI, Claude Code, etc.).
- ⚡ Connection pooling with lazy-spawn daemon (60s idle timeout).
- 🎛️ Tool filtering via
allowedToolsanddisabledToolsconfig. - � Server instructions support in output.
- �💡 Structured error messages with recovery suggestions.
The Context Problem
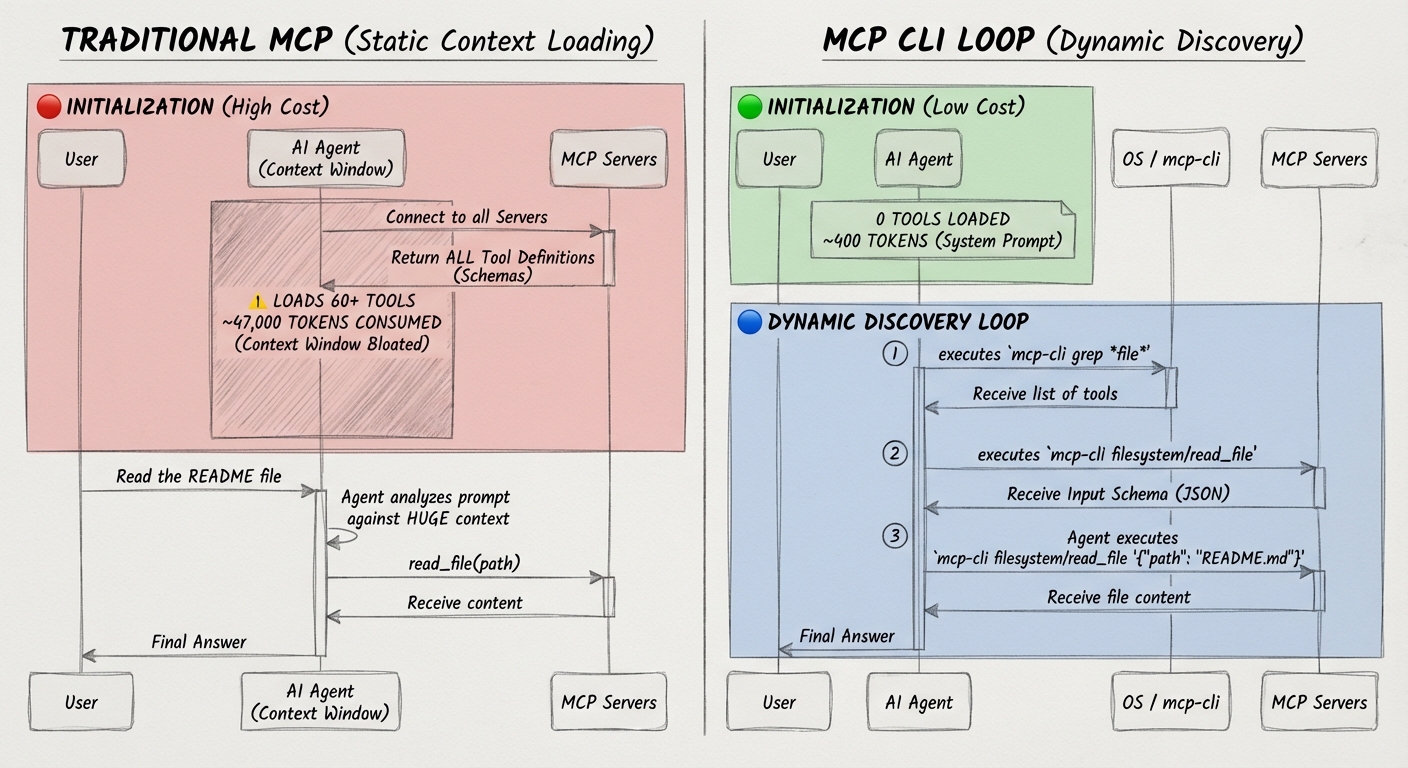
Every MCP server comes with tool definitions schemas describing what each tool does, its parameters, types, and descriptions. Traditional MCP integration loads all of these schemas upfront into the agent's context window.
Here's what that looks like in practice:
| Setup | Tokens Used |
|---|---|
| 6 MCP servers, 60 tools | ~47,000 tokens |
| After dynamic discovery | ~400 tokens |
That is a 99% reduction in MCP-related token usage for this scenario.
When working with multiple MCP servers (GitHub, databases, browser automation—tool), definitions quickly consume a third or more of the effective context. This leads to:
- Reduced effective context length for actual reasoning and code generation.
- More frequent context compactions interrupting flow.
- Hard limits on the number of simultaneous MCP servers you can use.
- Higher API costs due to input token overhead.
Dynamic Context Discovery
The solution is dynamic context discovery. Instead of loading everything upfront (static context), agents pull in only the information they need, when they need it.
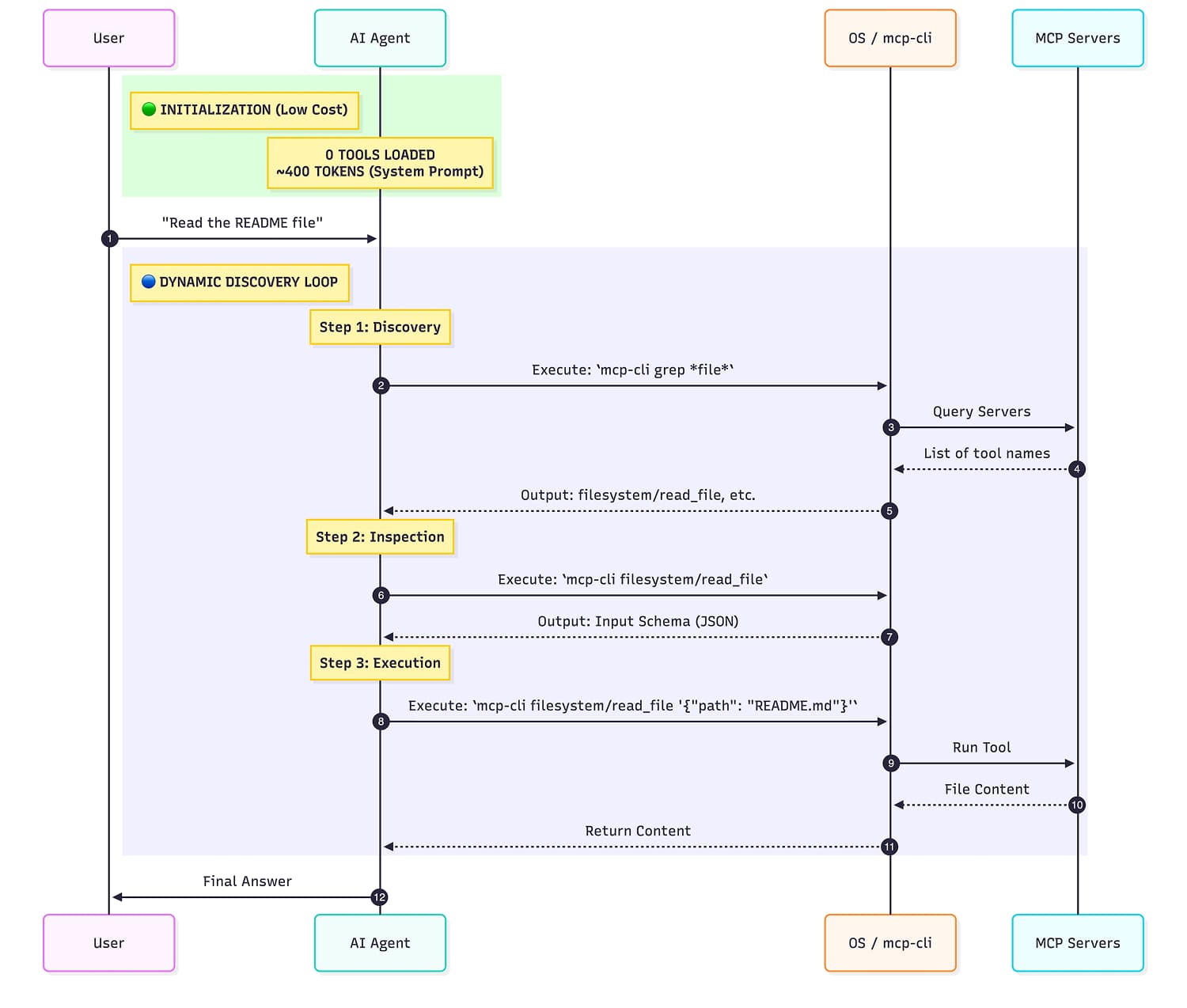
mcp-cli implements this pattern for MCP:
- Step 1: "What servers exist?" →
mcp-cli - Step 2: "What are the params for tool X?" →
mcp-cli info github search_repositories - Step 3: Execute →
mcp-cli call github search_repositories '{"query": "mcp"}'
Most Interactions only use a handful of tools, yet static loading consumes tokens for every tool definition. Dynamic discovery inverts this, you pay only for what you use.
Quick start
mcp-cli allows dynamic discovery of MCP while making tool interactions more efficient for AI coding agents.
1. Installation
# binary install
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/philschmid/mcp-cli/main/install.sh | bash
# requires bun install
bun install -g https://github.com/philschmid/mcp-cli2. Create a config file
Create mcp_servers.json in your current directory or ~/.config/mcp/:
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"."
]
},
"deepwiki": {
"url": "https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp"
}
}
}3. Discover available tools
# List all servers and tools
mcp-cli
# deepwiki
# • read_wiki_structure
# • read_wiki_contents
# • ask_question
#
# filesystem
# • read_file
# • read_text_file
# • read_media_file
# • read_multiple_files
# ...
# With descriptions
# mcp-cli -d4. Call a tool
# View tool schema first
mcp-cli info filesystem read_file
# Tool: read_file
# Server: filesystem
#
# Description:
# Read the complete contents of a file as text.
#
# Input Schema:
# {
# "type": "object",
# "properties": {
# ...5. Execute the tool
# Call the tool
mcp-cli call filesystem read_file '{"path": "./README.md"}'6. Complex commands
MCP CLI allows the model to generate commands that chain multiple tool calls together.
# Using a heredoc (no '-' needed with call subcommand)
mcp-cli call server tool <<EOF
{"content": "Text with 'single quotes' and \"double quotes\""}
EOF
# From a file
cat args.json | mcp-cli call server tool
# Using jq to build complex JSON
jq -n '{query: "mcp", filters: ["active", "starred"]}' | mcp-cli call github search
# Find all TypeScript files and read the first one
mcp-cli call filesystem search_files '{"path": "src/", "pattern": "*.ts"}' \
| jq -r '.content[0].text | split("\n")[0]' \
| xargs -I {} mcp-cli call filesystem read_file '{"path": "{}"}'Tool Filtering
You can restrict which tools are available from a server using allowedTools and disabledTools in your config:
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", "."],
"allowedTools": ["read_file", "list_directory"],
"disabledTools": ["delete_file"]
}
}
}Rules:
allowedTools: Only tools matching these patterns are available (supports glob:*,?)disabledTools: Tools matching these patterns are excludeddisabledToolstakes precedence overallowedTools- Filtering applies globally to all CLI operations (info, grep, call)
Examples:
# Only allow read operations
"allowedTools": ["read_*", "list_*", "search_*"]
# Allow all except destructive operations
"disabledTools": ["delete_*", "write_*", "create_*"]
# Combine: allow file operations but disable delete
"allowedTools": ["*file*"],
"disabledTools": ["delete_file"]Connection Pooling
By default, mcp-cli uses lazy-spawn connection pooling to avoid repeated MCP server startup latency:
- Automatic: No manual start/stop needed
- Per-server: Each MCP server gets its own daemon
- Stale detection: Config changes trigger re-spawn
- 60s idle timeout: Configurable via
MCP_DAEMON_TIMEOUT
Control via environment:
MCP_NO_DAEMON=1 mcp-cli info # Force fresh connection
MCP_DAEMON_TIMEOUT=120 mcp-cli # 2 minute idle timeoutIntegrating with AI Agents
mcp-cli is designed to be used with AI Agents and bash tools. There are two main ways to integrate it:
Option 1: System Instructions Integration
Add this to your AI agent's system prompt for direct CLI access:
## MCP Servers
You have access to MCP servers via the `mcp-cli` CLI.
Commands:
```bash
mcp-cli info # List all servers
mcp-cli info <server> # Show server tools
mcp-cli info <server> <tool> # Get tool schema
mcp-cli grep "<pattern>" # Search tools
mcp-cli call <server> <tool> # Call tool (stdin auto-detected)
mcp-cli call <server> <tool> '{}' # Call with JSON args
```
**Both formats work:** `info <server> <tool>` or `info <server>/<tool>`
Workflow:
1. **Discover**: `mcp-cli info` to see available servers
2. **Inspect**: `mcp-cli info <server> <tool>` to get the schema
3. **Execute**: `mcp-cli call <server> <tool> '{}'` with arguments
### Examples
```bash
# Call with inline JSON
mcp-cli call github search_repositories '{"query": "mcp server"}'
# Pipe from stdin (no '-' needed)
echo '{"path": "./file"}' | mcp-cli call filesystem read_file
# Heredoc for complex JSON
mcp-cli call server tool <<EOF
{"content": "Text with 'quotes'"}
EOF
```Option 2: Agent Skills
For AI agents that support Agent Skills an upcoming standard for extending coding agents. mcp-cli ships with a ready-to-use skill definition.
Create mcp-cli/SKILL.md in your agent's skills directory:
---
name: mcp-cli
description: Interface for MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers via CLI. Use when you need to interact with external tools, APIs, or data sources through MCP servers.
---
# MCP-CLI
Access MCP servers through the command line. MCP enables interaction with external systems like GitHub, filesystems, databases, and APIs.
## Commands
| Command | Output |
|---------|--------|
| `mcp-cli` | List all servers and tool names |
| `mcp-cli info <server>` | Show tools with parameters |
| `mcp-cli info <server> <tool>` | Get tool JSON schema |
| `mcp-cli grep "<pattern>"` | Search tools by name |
| `mcp-cli call <server> <tool> '{}'` | Call tool with arguments |
**Both formats work:** `info <server> <tool>` or `info <server>/<tool>`
**Add `-d` to include descriptions** (e.g., `mcp-cli info filesystem -d`)
## Workflow
1. **Discover**: `mcp-cli` → see available servers and tools
2. **Explore**: `mcp-cli info <server>` → see tools with parameters
3. **Inspect**: `mcp-cli info <server> <tool>` → get full JSON input schema
4. **Execute**: `mcp-cli call <server> <tool> '{}'` → run with arguments
## Examples
```bash
# List all servers and tool names
mcp-cli
# See all tools with parameters
mcp-cli info filesystem
# With descriptions (more verbose)
mcp-cli info filesystem -d
# Get JSON schema for specific tool
mcp-cli info filesystem read_file
# Call the tool
mcp-cli call filesystem read_file '{"path": "./README.md"}'
# Search for tools
mcp-cli grep "*file*"
# Complex JSON with quotes (use heredoc or stdin)
mcp-cli call server tool <<EOF
{"content": "Text with 'quotes' inside"}
EOF
# Or pipe from a file/command
cat args.json | mcp-cli call server tool
# Chain: search and read first result
mcp-cli call filesystem search_files '{"path": "src/", "pattern": "*.ts"}' \
| jq -r '.content[0].text | split("\n")[0]' \
| xargs -I {} mcp-cli call filesystem read_file '{"path": "{}"}'
```
## Options
| Flag | Purpose |
|------|---------|
| `-d` | Include descriptions |
| `-c <path>` | Custom config file path |
## Exit Codes
- `0`: Success
- `1`: Client error (bad args, missing config)
- `2`: Server error (tool failed)
- `3`: Network errorConclusion
The AI Agent space is moving incredibly fast. mcp-cli tries to solve context tool discovery problem turning it into an iterative, just-in-time process. It allows agents to access a massive ecosystem of shared capabilities without the context bloat of static integration. Whether used within a Skill or as a standalone utility, it ensures your agent spends its tokens on reasoning, not configuration.
The project is open source and designed to fit into existing workflows. Give it a try and contribute at github.com/philschmid/mcp-cli.
Thanks for reading! If you have any questions or feedback, please let me know on Twitter or LinkedIn.