Multimodal Function Calling with Gemini 3 and Interactions API
Building AI agents that can truly "see" requires more than just passing images in prompts. Coding agents need to read screenshots of UIs they're building. Computer use agents need to capture and analyze browser screenshots. Research agents need to process charts and diagrams from documents.
Multimodal function calling allows tools to return images the model can process natively, similar to how you pass images in prompts. Instead of describing what's in a file, your tool returns the actual image and Gemini 3 processes it natively.
This guide shows you how Multimodal Function Calling works using the Interactions API. The Interactions API is a unified interface for interacting with Gemini models and agents. It simplifies state management and tool orchestration, making it easy to build multi-turn agentic workflows.
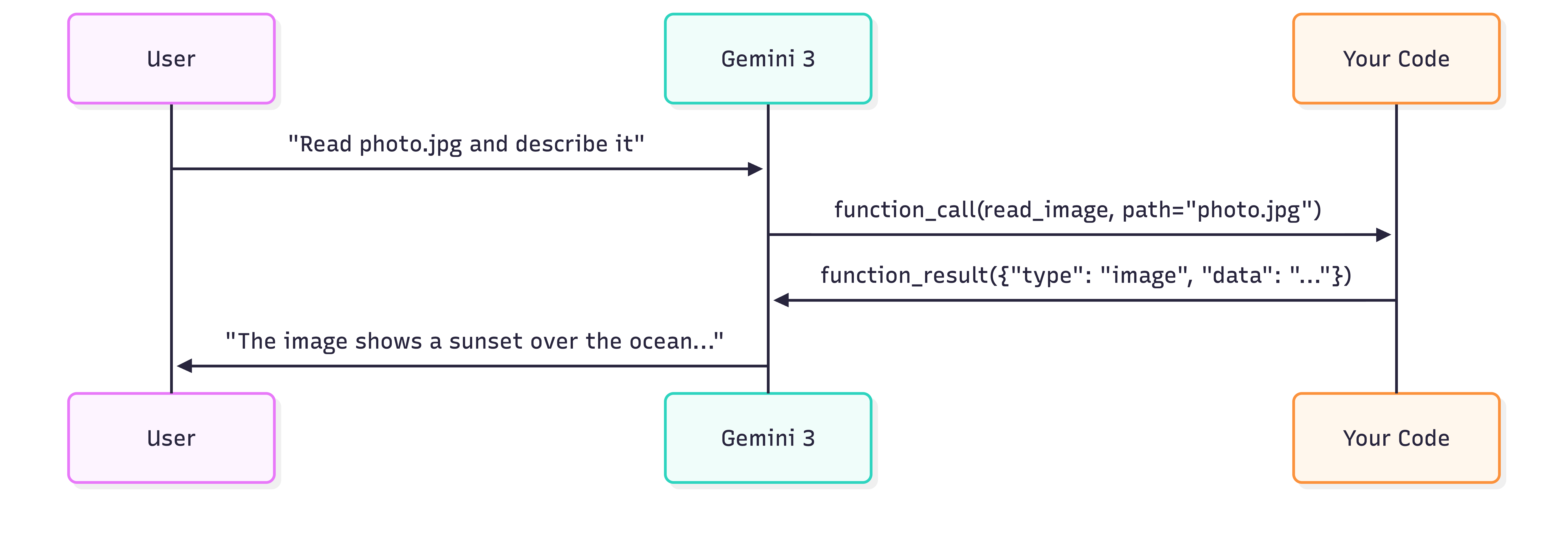
The key difference from standard function calling is in the function_result returns the actual image data. Gemini 3 processes this content natively—describing images, analyzing documents, or using visual information to make decisions.
{
"type": "function_result",
"call_id": "abc123",
"name": "read_image",
"result": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Additional context..."},
{"type": "image", "data": "<base64>", "mime_type": "image/png"}
]
}Example: Reading images from Fileystem
Let's build a tool that reads images from disk and returns them to the model for description. Get a Gemini API key and install the Google GenAI SDK:
pip install google-genaiSet your API key:
export GEMINI_API_KEY="your-api-key"1. Define the tool
read_image = {
"type": "function",
"name": "read_image",
"description": "Reads an image file from disk and returns its contents.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The path to the image file to read"
}
},
"required": ["path"]
}
}2. Implement the tool execution
import base64
from pathlib import Path
def execute_read_image(path: str) -> list[dict]:
"""Read image from disk and return as function result content."""
image_path = Path(path)
if not image_path.exists():
return [{"type": "text", "text": f"Error: Image not found at {path}"}]
mime_types = {
".jpg": "image/jpeg",
".jpeg": "image/jpeg",
".png": "image/png",
".webp": "image/webp",
}
mime_type = mime_types.get(image_path.suffix.lower(), "image/png")
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_path.read_bytes()).decode()
return [{"type": "image", "data": image_data, "mime_type": mime_type}]3. Create the agentic loop
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
image_path = "path/to/your/image.png"
prompt=f"Use the read_image tool to read '{image_path}' and describe what you see."
# Step 1: Send the initial request with our tool
interaction = client.interactions.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
input=prompt,
tools=[read_image],
)
# Step 2: Handle the function call
for output in interaction.outputs:
if output.type == "function_call" and output.name == "read_image":
image_result = execute_read_image(output.arguments.get("path"))
# Step 3: Send the image back to the model
interaction = client.interactions.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
input=[{
"type": "function_result",
"call_id": output.id,
"name": output.name,
"result": image_result, # Contains the image!
}],
tools=[read_image],
previous_interaction_id=interaction.id,
)
# Step 4: Get the model's description
for out in interaction.outputs:
if out.type == "text":
print(out.text)Concluding how it works
The interaction flow has four steps:
- User request → You send a prompt asking the model to use the tool
- Function call → Model responds with a
function_callspecifying which tool to use and arguments - Tool execution → You execute the tool and return the result (including the image)
- Model response → Model processes the image and generates a text description
# The function_call output from the model looks like:
{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "call_abc123",
"name": "read_image",
"arguments": {"path": "photo.jpg"}
}
# Your function_result response looks like:
{
"type": "function_result",
"call_id": "call_abc123",
"name": "read_image",
"result": [
{"type": "image", "data": "iVBORw0KGgo...", "mime_type": "image/png"}
]
}Conclusion
Multimodal function calling unlocks multimodal agentic use cases. By returning images directly in your function_result, you give Gemini 3 the ability to see what your tools see.
This pattern extends beyond file reading. You can build tools that capture screenshots, fetch images from APIs, render charts, or process scanned documents. Combined with the Interactions API's stateful sessions, you have everything you need to build sophisticated visual agents.
Next steps:
- Try the Interactions API quickstart notebook
- Explore Computer Use for browser automation with visual feedback
- Build tools that return PDFs or multiple images for complex document workflows
This API is in Beta, and we want your feedback! We're actively listening to developers to shape the future of this API. What features would help your agent workflows? What pain points are you experiencing? Please let me know on Twitter or LinkedIn.