AWS Lambda with custom docker images as runtime
It's the most wonderful time of the year. Of course, I'm not talking about Christmas but re:Invent. It is re:Invent time. Due to the current situation in the world, re:Invent does not take place like every year in Las Vegas but is entirely virtual and for free. This means that it is possible for everyone to attend. In addition to this, this year it lasts 3 weeks from 30.11.2020 to 18.12.2020. If you haven´t already registered do it here.

In the opening keynote, Andy Jassy presented the AWS Lambda Container Support, which allows you to use custom container (docker) images as a runtime for AWS Lambda. With that, we can build runtimes larger than the previous 250 MB limit, be it for "State-of-the-Art" NLP APIs with BERT or complex processing.

photo from the keynote by Andy Jassy, rights belong to Amazon
Furthermore, you can now configure AWS Lambda functions with up to 10 GB of Memory and 6 vCPUs.
In their blog post, Amazon explains how to use containers as a runtime for AWS lambda via the console.
But the blog post does not explain how to use custom docker images with the Serverless Application Model. For these
circumstances, I created this blog post.
Services included in this tutorial
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that lets you run code without managing servers. It executes your code only when required and scales automatically, from a few requests per day to thousands per second.
Amazon Elastic Container Registry
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a fully managed container registry. It allows us to store, manage, share docker container images. You can share docker containers privately within your organization or publicly worldwide for anyone.
AWS Serverless Application Model
The AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM) is an open-source framework and CLI
to build serverless applications on AWS. You define the application you want using yaml format. Afterwards, you build,
test, and deploy using the SAM CLI.
Tutorial
We are going to build an AWS Lambda with a docker container as runtime using the "AWS Serverless Application Model".
We create a new custom docker image using the presented Lambda Runtime API images.
What are we going to do:
- Install and setup
sam - Create a custom
dockerimage - Deploy a custom
dockerimage to ECR - Deploy AWS Lambda function with a custom
dockerimage
You can find the complete code in this Github repository.
Install and setup sam
AWS provides a
5 step guide on how to install
sam. In this tutorial, we are going to skip steps 1-3 and assume you already have an AWS Account, an IAM user with the
correct permission set up, and docker installed and setup otherwise check out this
link.
The easiest way is to create an IAM user with AdministratorAccess (but I don´t recommend this for production use
cases).
We are going to continue with step 4 "installing Homebrew". To install homebrew we run the following command in our terminal.
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"Note: Linux Users have to add Homebrew to your PATH by running the following commands.
test -d ~/.linuxbrew && eval $(~/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)
test -d /home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew && eval $(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)
test -r ~/.bash_profile && echo "eval \$($(brew --prefix)/bin/brew shellenv)" >>~/.bash_profile
echo "eval \$($(brew --prefix)/bin/brew shellenv)" >>~/.profileAfterwards we can run brew --version to verify that Homebrew is installed.
brew --versionThe fifth and last step is to install sam using homebrew. We can install the SAM CLI using brew install.
brew tap aws/tap
brew install aws-sam-cliAfter we installed it we have to make sure we have atleast version 1.13.0 installed
sam --version
# SAM CLI, version 1.13.0To update sam if you have it installed you can run brew upgrade aws-sam-cli.
brew upgrade aws-sam-cliCreate a custom docker image
After the setup, we are going to build a custom python docker image.
We create a app.py file and paste the following code into it.
import json
def handler(event, context):
body = {
"message": "Go Serverless v1.0! Your function executed successfully!",
"input": event
}
response = {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(body)
}
return responseTo containerize our Lambda Function, we create a dockerfile in the same directory and copy the following content.
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.8
# Copy function code
COPY app.py ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}
# Set the CMD to your handler (could also be done as a parameter override outside of the Dockerfile)
CMD [ "app.handler" ]Additionally we can add a .dockerignore file to exclude files from your container image.
Dockerfile
README.md
*.pyc
*.pyo
*.pyd
__pycache__
.pytest_cache
eventsTo build our custom docker image we run.
docker build -t docker-lambda .and then to test it we run
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 docker-lambdaAfterwards, in a separate terminal, we can then locally invoke the function using curl.
curl -XPOST "http://localhost:8080/2015-03-31/functions/function/invocations" -d '{"payload":"hello world!"}'
Deploy a custom docker image to ECR
Since we now have a local docker image we can deploy this to ECR. Therefore we need to create an ECR repository with
the name docker-lambda.
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name docker-lambdausing AWS CLI V1.x
To be able to push our images we need to login to ECR. We run an output ($()) from the command we retrieve from
ecr get-login. (Yes, the $ is intended).
$(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region eu-central-1)using AWS CLI V2.x
aws_region=eu-central-1
aws_account_id=891511646143
aws ecr get-login-password \
--region $aws_region \
| docker login \
--username AWS \
--password-stdin $aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.$aws_region.amazonaws.comread more here.
Next we need to tag / rename our previously created image to an ECR format. The format for this is
{AccountID}.dkr.ecr.{region}.amazonaws.com/{repository-name}
docker tag docker-lambda $aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.$aws_region.amazonaws.com/docker-lambdaTo check if it worked we can run docker images and should see an image with our tag as name

Finally, we push the image to ECR Registry.
docker push 891511646143.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/docker-lambdaDeploy AWS Lambda function with a custom docker image
Now, we can create our template.yaml to define our lambda function using our docker image. In the template.yaml we
include the configuration for our AWS Lambda function. I provide the complete template.yamlfor this example, but we go
through all the details we need for our docker image and leave out all standard configurations. If you want to learn
more about the sam template.yaml, you can read through the documentation
here.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: serverless-aws-lambda-custom-docker
# More info about Globals: https://github.com/awslabs/serverless-application-model/blob/master/docs/globals.rst
Globals:
Function:
Timeout: 3
Resources:
MyCustomDocker:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function # More info about Function Resource: https://github.com/awslabs/serverless-application-model/blob/master/versions/2016-10-31.md#awsserverlessfunction
Properties:
FunctionName: MyCustomDocker
ImageUri: 891511646143.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/docker-lambda:latest
PackageType: Image
Events:
HelloWorld:
Type: Api # More info about API Event Source: https://github.com/awslabs/serverless-application-model/blob/master/versions/2016-10-31.md#api
Properties:
Path: /hello
Method: get
Outputs:
# ServerlessRestApi is an implicit API created out of Events key under Serverless::Function
# Find out more about other implicit resources you can reference within SAM
# https://github.com/awslabs/serverless-application-model/blob/master/docs/internals/generated_resources.rst#api
MyCustomDockerApi:
Description: 'API Gateway endpoint URL for Prod stage for Hello World function'
Value: !Sub 'https://${ServerlessRestApi}.execute-api.${AWS::Region}.amazonaws.com/Prod/hello/'To use a docker image in our template.yaml we have to include the parameters ImageUri and PackageType in our
AWS::Serverless::Function resource. The ImageUri, as the name suggests is the URL to our docker image. For an ECR
image, the URL looks like this 123456789.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/myimage:latest, and for a public docker image
like that namespace/image:tag or docker.io/namespace/image:tag.
PackageType defines the type we provide to our AWS Lambda function, in our case an Image.
Afterwards, we can deploy our application again using sam deploy and thats it.
sam deploy --guidedThe Guided deployment will walk through all required parameters and will create a samconfig.toml afterwards for us.
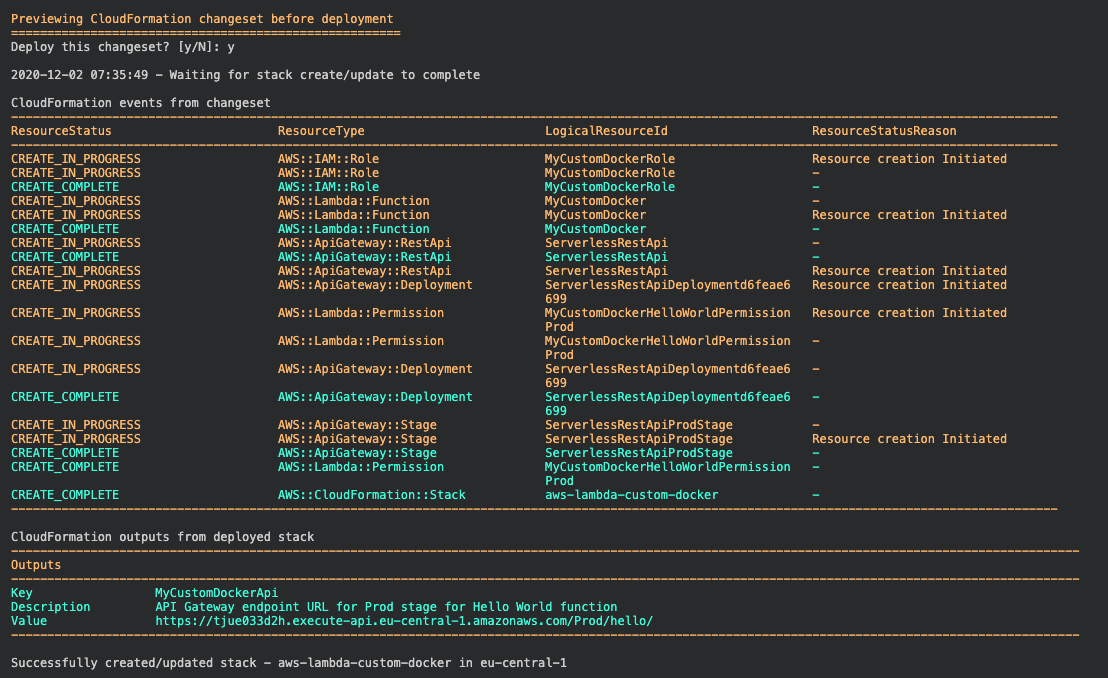
After the successfull deployment we should see something like this.
We take the URL from our API Gateway from the Outputs section and use any REST Client to test it.
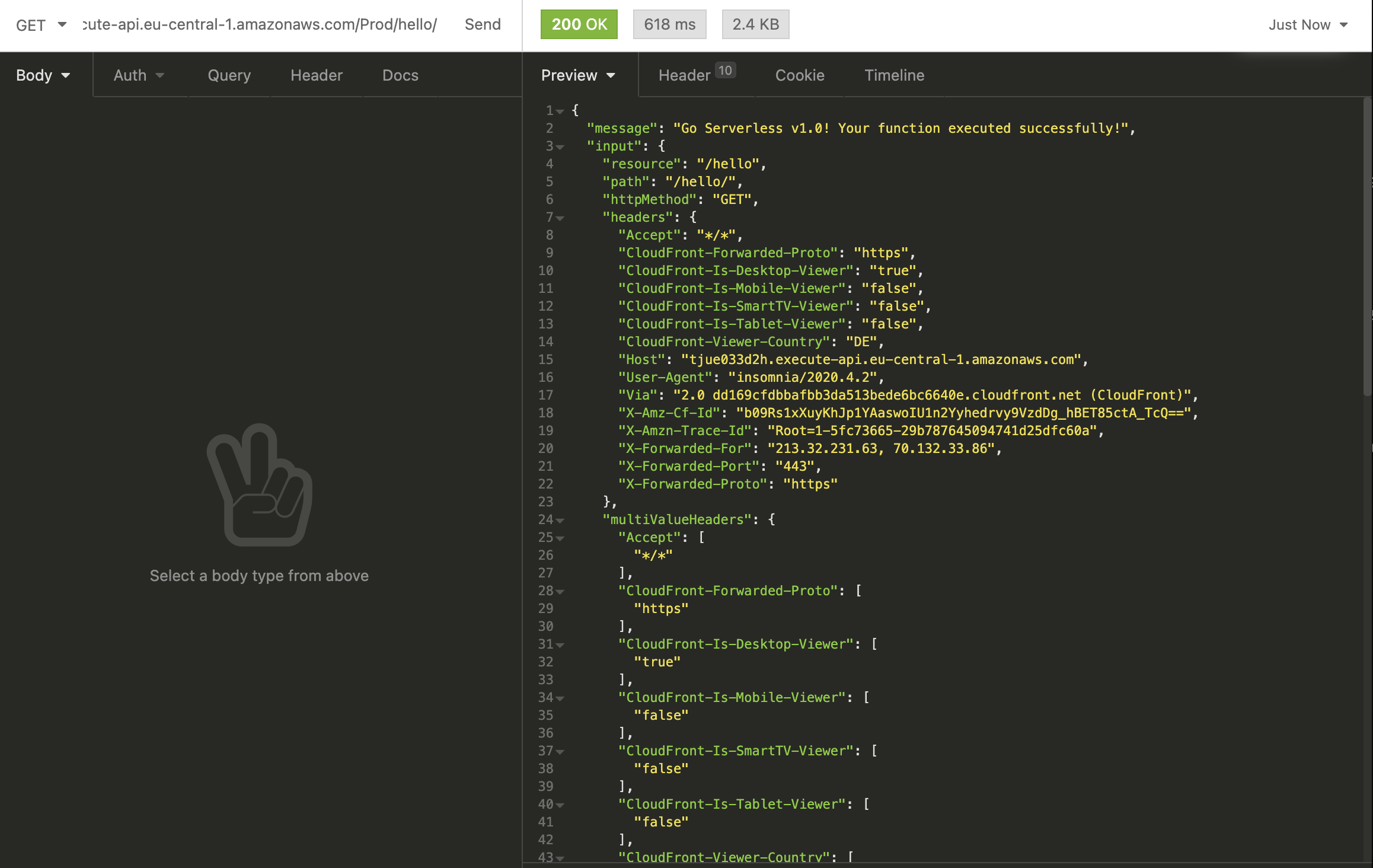
It worked. 🚀
We successfully deployed and created an AWS Lambda function with a custom docker image as runtime.
Conclusion
The release of the AWS Lambda Container Support enables much wider use of AWS Lambda and Serverless. It fixes many existing problems and gives us greater scope for the deployment of serverless applications.
Another area in which I see great potential is machine learning, as the custom runtime enables us to include larger machine learning models in our runtimes. The increase of configurable Memory and vCPUs boost this even more.
The future looks more than golden for AWS Lambda and Serverless.
You can find the GitHub repository with the complete code here.
Thanks for reading. If you have any questions, feel free to contact me or comment on this article. You can also connect with me on Twitter or LinkedIn.